IPC stands for International Patent Classification. It was created in 1971 by the Strasbourg Agreement. The PCB IPC standard provides a grading system using language-independent notation.
Today, more and more international companies are using this standard to demand quality delivery from suppliers. Especially in the absence of professional production engineers, IPC standards can enable suppliers to accurately identify customer requirements for quality.
IPC class definition
As the core of electronic products, PCB quality is the top priority. IPC divides PCB standards into three classes, they are class 1, class 2 and class 3. class 1 is the lowest quality requirement and class 3 is the highest. Therefore, no matter what industry and equipment is used, we can divide PCBS into the above three categories.
Here, we will look at the key elements of the three classes in order to provide our customers with quick guidance on quality requirements.
Class 1 – General Electronic Products
Such products are usually very simple, mostly used indoors, and have a short life cycle. More common are all kinds of cheap consumer electronics, such as TV remote controls, children’s toys and so on.
Class 2 – Dedicated Service Electronic products
Class 2 boards have more complex functions, higher life cycle and more stable operation requirements. In order to ensure the continuity of use, there are certain requirements for the accuracy of circuit board manufacturing and component placement. The two most common categories are smartphones and tablets.
Class 3–High-reliability Electronic Products
This type of product requires no downtime of any kind and must work accurately within the design process, regardless of the changing environment. Usually you can find them in military equipment, automation equipment and support system.
A-Level or IPC 6012 class 3 – Advanced Electronic Products
IPC 6012 Level 3 corresponds to products that typically operate in harsh environments while performing sophisticated calculations or requiring prolonged timely response, thus corresponding to the highest grade of electronic products. Typical applications are missile systems, submarine navigation systems, space shuttle communication modules and so on.

Different between Class 2 and Class 3 on assembly.
As mention above that Class 2 quality is lower than Class 3, what make them different?
- Barrel fill level
The components are secured to the PCB by solder paste, so as much solder paste as is allowed must be used to ensure a stronger fit.
Class 2 items usually consume half of the barrel, while Class 3 items consume three-quarters. Sometimes the reserved space in the through-hole is small, so it may be difficult to achieve this standard.
- Refined assembly
In order to achieve the high quality requirements of the class 3, the overall PCB assembly scheme must be designed specifically and ensure the optimal efficiency. Manufacturers need matching high-precision testing equipment to ensure the accuracy of assembly.
- Installation and cleanliness
Due to the specific production process, the surfaces of the three types of products and the welding feet of the components are neat and clean.
For products working in harsh environments, there may even be special surface treatment requirements, and the customer may designate a special supplier for the PCBA manufacturer to handle.

At the same time, because the class3 products are widely used in high precision calculation, real-time and rapid response and other applications, so the installation does not allow for any mistakes.
Difference between class 2 and class 3 on pcb bare board
For the class 2 , the required number of holes in the copper plating layer cannot exceed 5%; And the requirements of the three categories can not be hollow. These uncontrolled holes can lead to abnormal current, or affect the work of some sensitive components.
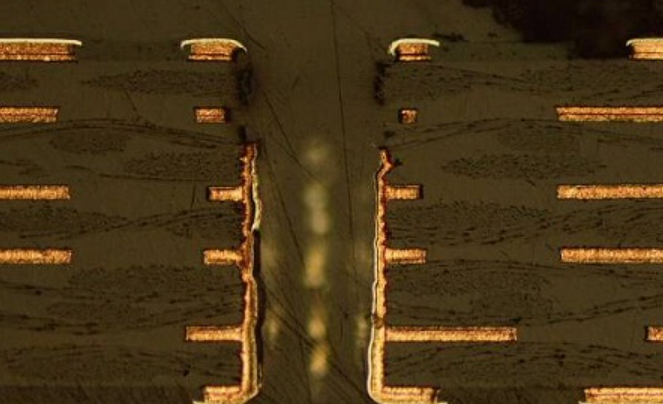

Regarding to plating thickness, Class 3 requires 1 mil while Class 2 requires 2 mils.
Summary
It is very important to ensure that your PCBA is designed to meet the IPC standards. Especially for new projects, sometimes the engineers are not familiar with production or have no corresponding project experience. In this case, IPC standard is a very good guide for production design.
Of course, it is also necessary to establish early relationships with suppliers. Fumax provides Design for Manufacturing (DFM) service to help your project move quickly from prototype to mass production.
