The motor PCB packaging process is a process technology used to package electronic components and PCB boards in motor control systems.
It can improve the performance, stability and reliability of the motor, and can also improve the production efficiency and quality of the motor. This article will introduce in detail the technical points and steps of the motor PCB packaging process.
The background and significance of motor PCB packaging process
With the continuous development of electronic technology, motor control systems are becoming more and more complex, requiring more and more electronic components to be integrated onto PCB boards. In order to improve the performance, stability and reliability of the motor, as well as to improve the production efficiency and quality of the motor, the motor PCB packaging process came into being. The motor PCB packaging process can reliably connect electronic components to the PCB board, so that the electronic components can be optimally laid out and connected on the PCB board, thereby achieving optimal control and efficient operation of the motor.
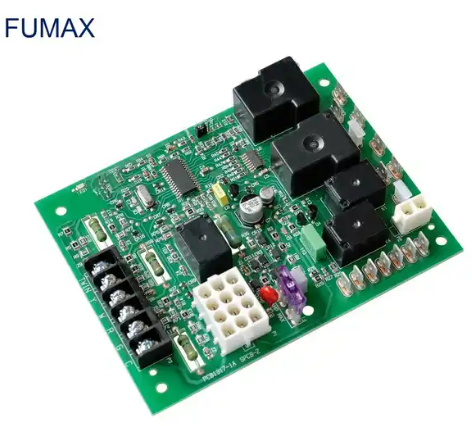

Motor PCB packaging process process
The motor PCB packaging process includes the following steps:
- Board layout: According to the model and specifications of the motor, lay out and arrange the electronic components and PCB board to determine the connection method and position between them.
- Component placement: Place the electronic components on the PCB board one by one in the order and position of the board, and use a professional placement machine for fixation and connection.
- Welding: Use welding tools to weld the electronic components to the PCB board to ensure the reliability and stability of the connection.
- Inspection: Inspect the welded PCB boards to check whether there are short circuits, open circuits, virtual soldering and other problems, and repair or replace unqualified PCB boards.
- Encapsulation: Use professional packaging equipment to encapsulate the PCB board to protect its internal electronic components from the influence and damage of the external environment.
- Test: Test the packaged motor PCB to check whether its performance and reliability meet the requirements.
Technical points of motor PCB packaging process
The technical points of the motor PCB packaging process include the following aspects:
- Layout: A reasonable layout can improve the performance and stability of the motor. Therefore, when making boards, it is necessary to consider the interaction between electronic components and the reliability of signal transmission, and conduct a reasonable layout and arrangement of electronic components.
- Connection: Reliable connection can ensure the stable operation of the motor. Therefore, when mounting and welding components, you need to pay attention to the quality and stability of the connection between the electronic components and the PCB board to avoid problems such as virtual soldering and missing soldering.
- Thermal design: Good thermal design can ensure the cooling effect and reliability of the motor. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the heat generation and heat dissipation methods of electronic components when mounting and packaging components to ensure that the motor can operate normally in a high-temperature environment.
- Electromagnetic shielding: Good electromagnetic shielding can ensure the signal transmission quality and stability of the motor. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the electromagnetic interference and shielding effect between electronic components when selecting and laying out components to avoid problems such as signal interference and distortion.
- Reliability: In order to ensure the stability and reliability of the motor, the motor PCB needs to be strictly inspected and tested, including appearance inspection, performance testing, environmental testing and other aspects. At the same time, unqualified PCBs need to be repaired or replaced to ensure their quality and reliability.
Summarize
The motor PCB packaging process is an important motor control system manufacturing technology. It can improve the performance, stability and reliability of the motor, and also improve the production efficiency and quality of the motor.
In order to ensure the quality and reliability of motor PCB packaging, strict control and management are required throughout the entire manufacturing process, including board making, component placement, welding, inspection, packaging and testing. Only by doing a good job in each link can the stability and reliability of the motor be guaranteed.