This article mainly introduces the PCB design for bus MCU motor controller. PCB design is an important part of the motor controller and needs to consider factors such as layout, signal integrity, power integrity, thermal design, and electromagnetic interference prevention.
Through reasonable PCB design, the performance and reliability of the motor controller can be improved so that it can better meet the needs of the bus drive system.
introduction
With the continuous development of science and technology, motor controllers are increasingly used in various industries. Especially in the bus drive system, the role of the motor controller is crucial. As an important link in the design of motor controller, PCB design directly affects the performance and stability of the controller. This article aims to discuss the PCB design for bus MCU motor controller.
Motor Controller Overview
A motor controller is a device used to control the operation of a motor. It controls the motor speed and torque by adjusting the input current and voltage of the motor. Motor controllers generally consist of power electronic devices, control circuits, protection circuits, interface circuits, etc. In the bus drive system, the motor controller needs to withstand high current and voltage, so its design and manufacturing require special attention to safety and reliability.
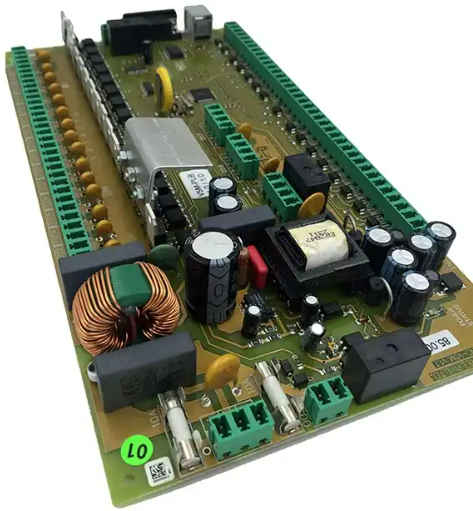

PCB design essentials
Layout design
Layout design is a key link in PCB design, and factors such as signal integrity, power distribution, and thermal design need to be considered. In layout design, analog circuits and digital circuits need to be laid out separately, taking into account signal shielding and preventing interference. In addition, power cords need to be distributed reasonably to ensure the stability and reliability of the power supply.
Signal integrity design
Signal integrity means that the signal is not distorted, delayed, or distorted during transmission. In PCB design, factors such as signal transmission line effects, reflections, and crosstalk need to be considered to ensure signal integrity. For these factors, corresponding measures can be taken, such as selecting the appropriate transmission line type, adding matching resistors, optimizing wiring, etc.
Power supply integrity design
Power supply integrity means that the power supply does not fluctuate, interfere with, or power outage during the power supply process. In PCB design, factors such as power supply stability, noise, and filtering need to be considered to ensure the integrity of the power supply. To address these factors, corresponding measures can be taken, such as selecting appropriate power modules, adding filter capacitors, optimizing power wiring, etc.
Thermal design
Thermal design is a key factor to ensure the normal operation of the motor controller in high temperature environments. In PCB design, factors such as the heat generation and heat dissipation method of the device need to be considered to ensure that the temperature of the controller does not exceed the specified range. In response to these factors, corresponding measures can be taken, such as optimizing device layout, adding heat sinks, etc.
Anti-electromagnetic interference design
Electromagnetic interference will adversely affect the performance of the motor controller, so anti-electromagnetic interference design is required in PCB design. Measures such as shielding, filtering, and grounding can be used to reduce the impact of electromagnetic interference.
Design Flow
- Requirements analysis: Understand the performance requirements, working environment and other conditions of the motor controller, and clarify the design goals.
- Solution design: Based on the demand analysis results, select an appropriate solution, including power electronic devices, control circuits, protection circuits, etc.
- PCB layout design: Carry out PCB layout design based on the solution design results, taking into account factors such as signal integrity and power integrity.
- PCB wiring design: Carry out PCB wiring design based on the layout design results, taking into account factors such as signal integrity and power integrity.
- PCB post-processing: PCB post-processing, including anti-electromagnetic interference design, thermal design, etc.
- Sample production and testing: Make PCB samples, conduct performance testing and reliability testing, and verify the correctness and reliability of the design.
- Optimization and improvement: Based on test results, the design is optimized and improved to improve performance and reliability.
- Mass production: After optimization and improvement, mass production is carried out to meet market demand.
in conclusion
This article mainly discusses the PCB design for bus MCU motor controller. Through the introduction of the motor controller overview and the analysis of PCB design points, the corresponding design process is proposed. Through reasonable layout design and wiring design, as well as anti-electromagnetic interference design and thermal design, the performance and reliability of the motor controller can be effectively improved so that it can better meet the needs of the bus drive system.
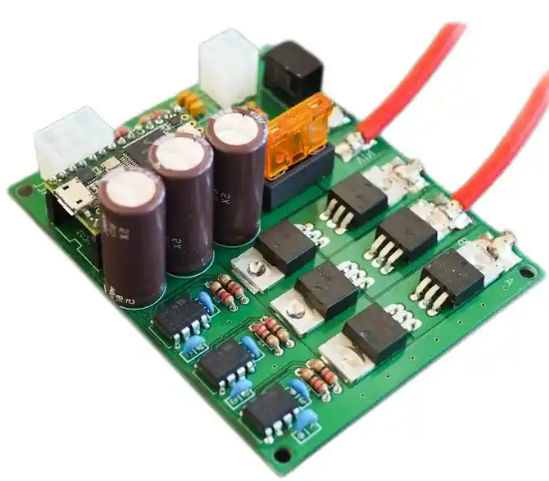
With the continuous development of science and technology, the performance and power density of motors have also continued to improve, which has also put forward higher requirements for the control system of the motor. Therefore, the PCB design of the motor controller also needs to be continuously researched and improved to adapt to the ever-increasing performance requirements.
At the same time, the stability and reliability of the system are ensured to provide guarantee for the safe operation of buses.