PCB assembly, a critical phase in electronic manufacturing, is susceptible to various uncommon errors that are often overlooked but can significantly impact the quality and functionality of electronic devices. Beyond the common defects, understanding these less frequently occurring issues and their root causes is essential for fostering a comprehensive approach to quality assurance and process improvement in PCB assembly.
Component Misorientation:
One less common but potentially impactful error in PCB assembly is component misorientation, where components are placed on the board with incorrect rotational alignment. This error can arise due to human error during manual assembly, misinterpretation of component orientation markings, or malfunctioning of automated pick-and-place machines. The consequences of component misorientation include electrical shorts, intermittent connections, and compromised functionality of the assembled PCB. Addressing this issue requires meticulous operator training, effective visual inspection protocols, and the implementation of advanced machine vision systems to verify component orientation prior to placement.
Insufficient Solder Paste Stencil Aperture Release:
In the surface mount technology (SMT) process, the solder paste stencil plays a pivotal role in ensuring precise deposition of solder paste onto the PCB. However, an uncommon yet critical issue that may arise is insufficient release of solder paste from the stencil apertures, leading to incomplete or inconsistent solder deposits during the reflow soldering process. This issue can be attributed to stencil fabrication imperfections, inadequate solder paste rheology, or improper handling and storage of solder paste. Mitigating this error entails stringent quality control measures during stencil fabrication, rheological characterization of solder paste, and adherence to proper storage and handling practices to optimize solder paste release and deposition.
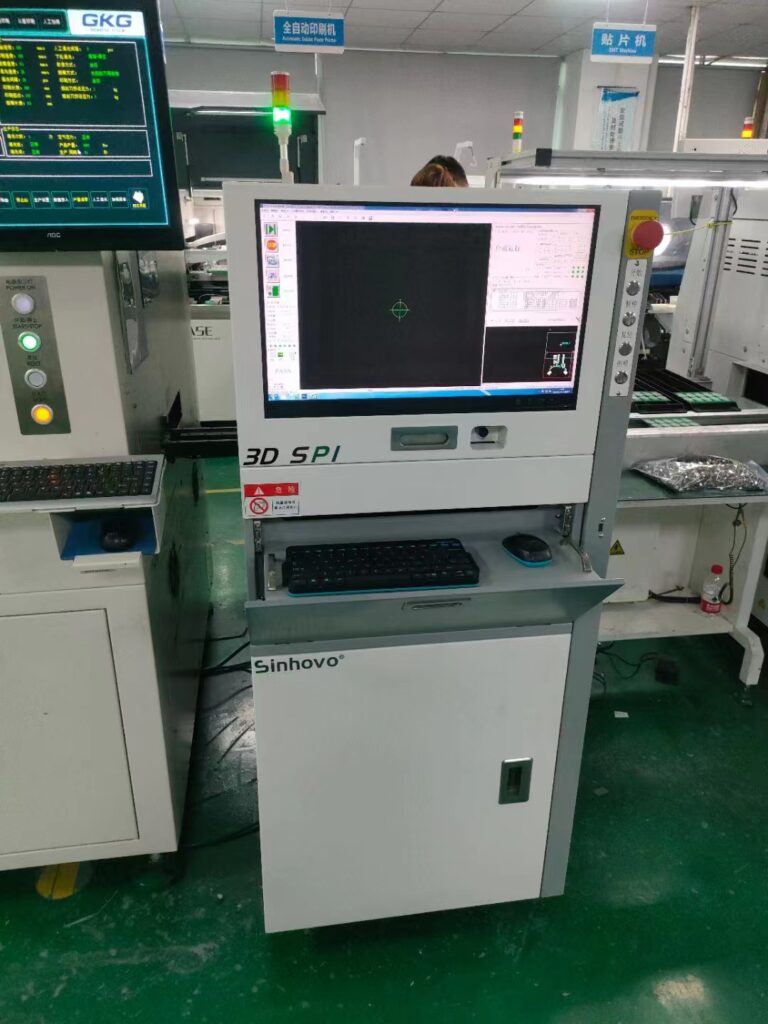
In modern SMT production workshops, 3D SPI equipment is usually used to ensure the quality of solder paste printing.

Incomplete Through-Hole Component Insertion:
In assemblies involving through-hole components, incomplete insertion of leads into the PCB can pose a less frequent yet significant challenge. This error may occur due to variations in component lead dimensions, insufficient insertion force during automated assembly, or inadequate clearance in plated through-holes. Incomplete through-hole component insertion can result in intermittent electrical connections, mechanical instability, and compromised reliability of the final assembly. To mitigate this issue, manufacturers must implement precise lead dimension tolerance control, optimize insertion force parameters, and conduct thorough post-insertion inspections to ensure complete and secure seating of through-hole components.
Inadequate Conformal Coating Coverage:
Conformal coating is applied to PCB assemblies to protect them from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants. However, an uncommon yet critical error that may occur is inadequate coverage of the PCB surface with conformal coating, leaving certain areas vulnerable to environmental stressors. This issue can stem from uneven coating application, improper viscosity control of the coating material, or inadequate curing of the coating. Insufficient conformal coating coverage can compromise the long-term reliability and robustness of the assembled PCB. Addressing this challenge necessitates meticulous coating process optimization, real-time monitoring of coating thickness and uniformity, and rigorous validation of coating integrity through advanced inspection techniques.

Conclusion:
Uncovering the uncommon errors in PCB assembly process and understanding their underlying causes is indispensable for fostering a holistic approach to quality assurance and process enhancement. By addressing these less frequently occurring issues, manufacturers can fortify their production processes, elevate the reliability of electronic devices, and uphold the highest standards of quality in the dynamic landscape of electronic manufacturing. Embracing a proactive stance towards mitigating uncommon errors empowers manufacturers to cultivate a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, driving the industry forward and ensuring the delivery of superior electronic products to the market.