Requirements and standards for motor drive control board PCB design
The requirements and standards for motor drive control board PCB design need to be based on user needs and PC production process standards. Customers need to provide relevant BOM files and PCB files.
The requirements and standards for motor drive control board PCB design mainly include the following aspects:
Layout optimization: Good layout design can reduce electromagnetic interference and improve circuit stability. Specific requirements for layout optimization include:
- Sufficient distance should be maintained between the motor drive circuit and the logic/control circuit to reduce mutual interference.
- Minimize the loop area, that is, place the input and output terminals close to one side to prevent interference caused by loop induction.
- In PCB layout, attention should be paid to the design of the ground wire, and the return path of the ground wire should be shortened as much as possible to reduce the inductance.
- Pay attention to the separation of analog and digital parts and arrange them in different areas.
Signal integrity: In motor drive PCB design, signal integrity is a key issue. To ensure the stability and reliability of signal transmission, the following points can be considered:
- For long-line transmission, pay attention to impedance matching and choose appropriate transmission lines and differential signal transmission to reduce reflections and crosstalk on the transmission lines.
- For high-speed signal transmission, attention should be paid to the routing and routing rules of signal lines to avoid signal integrity problems caused by too long signal return paths.
- Using appropriate terminal resistors and shielding designs can effectively reduce signal interference and noise.

Power consumption control: Power consumption control in motor drive PCB design is crucial to improve the efficiency of the device and extend battery life. To achieve power consumption control, you can start from many aspects:
- Choose low-power components, such as low-power MOSFETs and power management chips.
- Optimize the power supply layout, reduce the length of the power consumption loop, reduce the resistance of the wires, and improve the efficiency of the power supply.
- Reasonably design the power management module to realize dynamic power consumption management of the motor, and adjust the power supply and working mode of the motor according to actual needs.
Component and circuit protection: For motor drive control board PCB design, circuit protection measures need to be considered to prevent abnormal conditions such as overcurrent, overvoltage, and overheating from causing damage to the circuit and components. Specific measures include:
- Add overcurrent protection components, such as fuses or PTC devices, to protect the circuit from overcurrent.
- Add components such as a surge suppressor or varistor at the power input end to absorb transient high voltage and protect the circuit from overvoltage.
- Reasonably design the heat dissipation structure, such as using thermally conductive materials and radiators to conduct heat away from the heating components to maintain the normal operating temperature of the circuit.
Mechanical structure requirements: The design of the motor drive control board PCB also needs to consider the requirements related to the mechanical structure to ensure that the PCB can be installed correctly and work with the mechanical components. Specific requirements include:
- PCB size and shape should match the mechanical structure to meet installation and fixing requirements.
- The PCB needs to reserve interfaces and holes for connecting to mechanical components (such as bearings, motors, radiators, etc.).
- The edges of the PCB should be chamfered or otherwise processed to avoid injury to the operator or damage to other components due to sharp edges.
Maintainability and testability: The motor drive control board PCB design should consider maintainability and testability requirements to ensure that the circuit board can be easily repaired and tested during production and use. Specific requirements include:
- Reserve test interfaces and test points on the PCB to facilitate functional testing and fault location during the production process.
- The PCB should be clearly marked with the identification and function description of each component so that maintenance personnel can quickly identify and understand the components and connection relationships on the circuit board.
Motor control unit PCB assembly
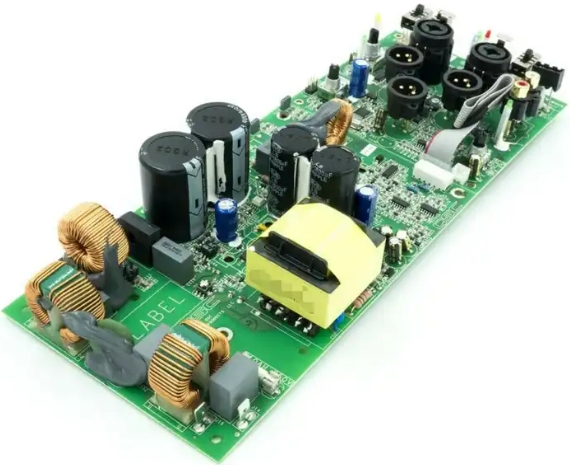

The process of motor control unit PCB assembly includes the following steps:
- Prepare materials: According to the schematic diagram and PCB board diagram of the motor control unit, prepare the required electronic components, PCB board, solder, wires and other auxiliary materials.
- Pre-assembly inspection: Check whether the PCB board has any defects or bad phenomena, such as short circuit, open circuit, missing components, etc. At the same time, check whether the quality and specifications of components meet the requirements.
- Layout design: Carry out layout design of the motor control unit based on the schematic diagram and actual needs. Layout design should consider circuit complexity, electromagnetic compatibility, signal integrity and other factors, while also following PCB wiring rules and standards.
- Component welding: According to the layout design, the electronic components are welded to the PCB board one by one according to the requirements of the schematic diagram. During the welding process, attention should be paid to issues such as welding quality, component polarity and temperature control.
- Wire connection: According to the circuit diagram and actual needs, connect the wires on the PCB board to realize the electrical connection of the motor control unit. Wire connections must follow the requirements of the circuit diagram, use appropriate wire diameters and connectors, and pay attention to the quality and insulation of the connectors.
- Debugging and testing: After completing the PCB assembly, the motor control unit must be debugged and tested to ensure its normal operation. Debugging and testing include functional testing, performance testing, electromagnetic compatibility testing, etc.
- Quality inspection: Conduct quality inspection on the motor control unit, including appearance inspection, electrical performance inspection, safety performance inspection, etc. If problems are found, repair and improve them in a timely manner.
- Packaging and delivery: After quality inspection, the motor control unit is packaged and delivered to the customer or user. Packaging should take factors such as shockproof, moisture-proof, and dustproof into consideration to ensure that the product is not damaged during transportation.
The above are the general steps for motor control unit PCB assembly. The specific steps may vary depending on product requirements and actual conditions. Pay attention to safety and quality control during the assembly process and follow relevant standards and specifications.